Distribution of Granite Landforms in China
Granite is abundant across the Earth's surface. China stands out as one of the countries with the most extensive granite formations, which span an impressive 909,000 square kilometers, accounting for 10% of the nation's territorial area. China boasts over 40 remarkable granite landforms, predominantly found in the Altay Mountains, Tianshan Mountains, Kunlun Mountains-Qilian Mountains, Yin Mountains-Daxing'anling Prefecture, Qin Mountains-Mount Taishan, southeast coastal areas, etc. Granite landforms exhibit prominent variations across different regions characterized by distinct climates. By climate, granite landform zones in China can be categorized into half-dry and half-wet (I), dry (II), freeze-thaw (III), and wet and hot (IV) zones. Granite landforms in China can also be categorized based on their distinct characteristics. These include granite landforms featuring high mountains with jagged peaks and deep valleys (exemplified by Mount Huangshan), granite landforms featuring high mountains with steep cliffs (exemplified by Mount Huashan), granite landforms featuring low dome-shaped mountains (exemplified by mountains in Heshigten), granite landforms shaped by marine abrasion (exemplified by stone landscapes in Pingtan Island), granite landforms shaped by wind erosion (exemplified by Guai Shi Gou in Bole City), granite landforms featuring dogtooth-shaped ridges (exemplified by Mount Lao), granite landforms featuring round peaks and long ridges (exemplified by Mount Heng), and granite landforms featuring caves (exemplified by Fuan cave-type granite landscapes).
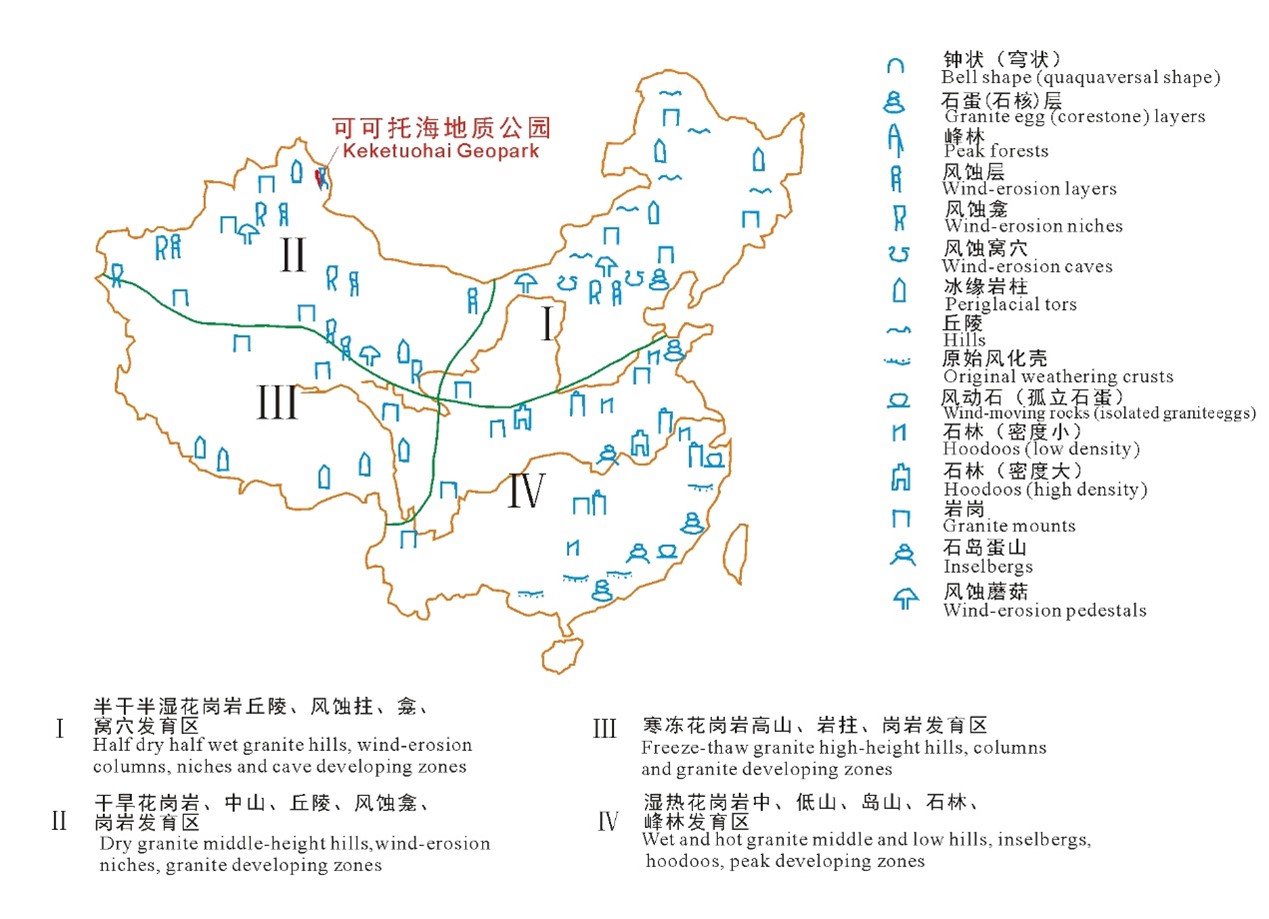 Distribution of Various
Granite Landform Development Zones in China
Distribution of Various
Granite Landform Development Zones in China
