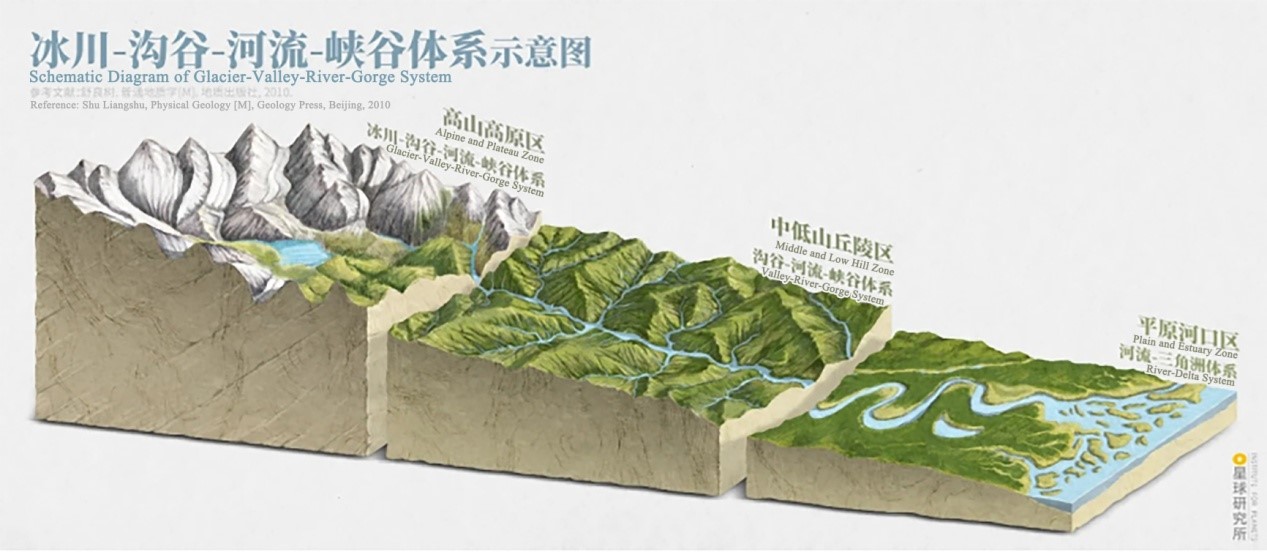
What are Granite Gorge Landforms?
In granite areas, valleys
characterized by steep slopes and a depth greater than their width are commonly
known as granite canyon landforms. Granite canyon landforms typically form in
areas where tectonic fractures occur and the ground is uplifted due to
neotectonic movement. These landforms take shape most easily when the velocity
of ground uplift is coordinated with the rate of down-cutting. The Holy Bell
Gorge was formed during the orogenic activity of the Altay Mountains. The
lateral and downward erosion of flowing water along fissures and collapses
resulted in the initial shape of the gorge. As granite masses were uplifted to
higher altitudes, they underwent the erosive effects of ice and snow, as well
as the combined influence of pinnate drainage patterns, melted ice and snow,
and frost weathering. This transformative process resulted in a narrow gorge
with considerably deep and steep slopes, representing the ideal stage for the
creation of granite gorge landscapes.