Fuyun Earthquake
On August 11, 1931, the
sudden movement of the Keketuohai-Ertai active fault zone caused a great
earthquake with a moment magnitude scale measured 8.0 along the Kalaxiangeer
geopark. With strong ground shaking, the earthquake rocked places stretching
thousands of kilometers. It could be felt strongly in Semipalatinsk of the
Soviet Union in the west, Inner Mongolia in the east, and Lanzhou, China, in
the southeast. A surface fault zone with a length of about 176 kilometers and a
strike of 342° is formed in the area from Kayierte River to the northern slope
of Aermante Mount,
resulting in a horizontal displacement of 3-15 meters. The fault escarp is
0.3-5 meters high, with some sections reaching as high as 16.5-60 meters. The
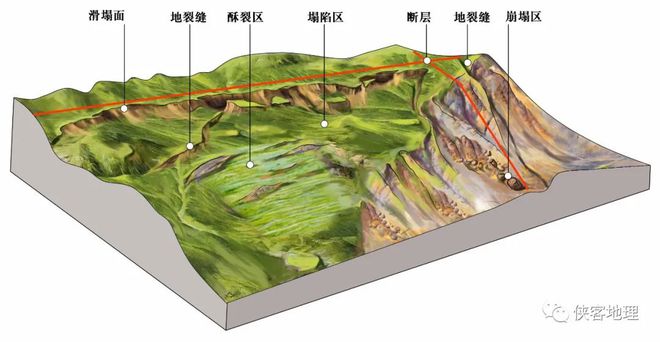
fault cuts through a series of geological landforms such as the water system,
gullies, ridges, and talus, forming various macro earthquake remains such as
earthquake cracks, subsidence areas, earthquake rift troughs, and offset
streams, as well as micro earthquake remains such as earthquake scarps,
earthquake eyebrow ridges, landslides, ridges, trenches, fault sag ponds,
bulges, dislocated talus, and earthquake rupture. Although more than 90 years
have passed, these earthquake remains are well preserved.